Solar System Travel Time Calculator
Related
Space Travel Time Calculator – Solar System Travel Time Calculator
🛰️ What is a Space Travel Time Calculator?
A Space Travel Time Calculator is an interactive online tool that estimates how long it would take to reach various planets, moons, or even nearby stars — based on your chosen travel speed in kilometers per hour.
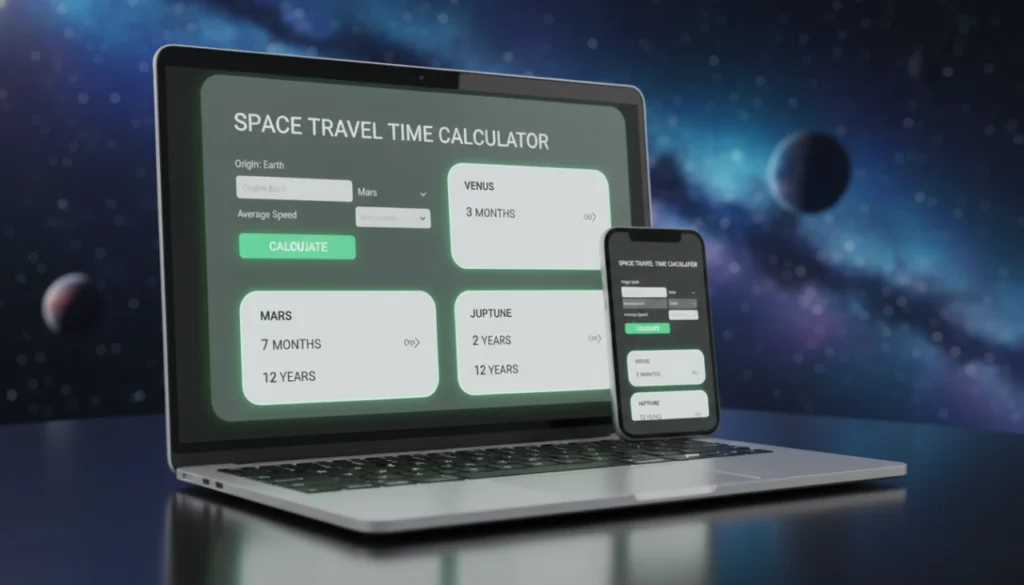
By entering a spacecraft’s speed, this calculator gives you a realistic idea of the time duration (in years, months, and days) it would take to travel from Earth to destinations like the Moon, Mars, Jupiter, or Alpha Centauri.
It’s a fun yet educational tool for astronomy enthusiasts, students, and science content creators who want to visualize the enormous distances in space.
Here’s a clear and SEO-friendly explanation you can use for your “How to Calculate Space Travel Time” section — perfect for your calculator page 👇
How to Calculate Space Travel Time
Calculating how long it would take to reach another planet depends on three main factors: distance, speed, and travel path.
- Find the average distance between Earth and the destination planet.
- For example, Mars is about 225 million km from Earth (on average).
- Determine your spacecraft’s speed.
- Example: If a spacecraft travels at 58,000 km/h, divide the distance by the speed.
- Apply the basic time formula:
Adjust for orbital alignment:
- Planets move around the Sun, so the distance varies. Real missions use the shortest path called a Hohmann transfer orbit.
Example Calculation:
\(\text{Time} = \frac{225{,}000{,}000 \text{ km}}{58{,}000 \text{ km/h}} \approx 3{,}879 \text{ hours (≈162 days)}\)🌍 How Does the Space Travel Time Calculator Work?
The calculator uses a simple mathematical relationship between distance and speed:
\(\text{Time} = \frac{\text{Distance}}{\text{Speed}}\)Here:
- Distance is measured in kilometers (km)
- Speed is your spacecraft’s velocity (km/h)
- Time is the total travel time in hours, which is then converted into years, months, and days.
Example:
If your speed = 40,000 km/h (similar to fast spacecraft speeds):
\(\text{Time} = \frac{225,000,000}{40,000} = 5625 \text{ hours}\)Now convert 5625 hours into days and years:
\(5625 \div 24 = 234.37 \text{ days} \approx 0.64 \text{ years}\)So, at 40,000 km/h, it would take around 0.6 Earth years (about 7.5 months) to reach Mars (on average).
🪐 Approximate Average Distances from Earth
Below are some average planetary distances (which constantly vary due to orbital positions):
- 🌕 Moon – 384,400 km
- 🌅 Venus – 261 million km
- 🔴 Mars – 225 million km
- 🪐 Jupiter – 778.5 million km
- 💫 Saturn – 1.43 billion km
- 🌊 Neptune – 4.49 billion km
- ⭐ Alpha Centauri (Nearest Star) – 41.3 trillion km
💡 How to Use the Space Travel Time Calculator
- Enter your speed in the input box (in km/h).
Example: 40,000 for a fast spacecraft, or 100,000 for an advanced one. - Click “Calculate Travel Times.”
- Instantly view travel time cards showing how long it would take to reach:
- The Moon
- Mars
- Jupiter
- Saturn
- Neptune
- Alpha Centauri
- Use the “Copy” button to save each travel time result for sharing or research.
It’s that simple — no login, no complex setup, and 100% browser-based.
🪐 Planetary Orbital Periods and Conversion Formulas
Even though the calculator focuses on travel time, it’s useful to understand each planet’s orbital period — that is, how long one year is on that planet compared to Earth.
\(\text{Mercury Year} = \frac{88}{365.25} \times \text{Earth Year}\)
\(\text{Venus Year} = \frac{225}{365.25} \times \text{Earth Year}\)
\(\text{Mars Year} = \frac{687}{365.25} \times \text{Earth Year}\)
\(\text{Jupiter Year} = \frac{4333}{365.25} \times \text{Earth Year}\)
\(\text{Saturn Year} = \frac{10759}{365.25} \times \text{Earth Year}\)
This helps visualize how time and age differ when compared to Earth — a core idea also used in “Age on Other Planets” calculators.
🌠 Why This Calculator is Fascinating
- Helps understand space distances visually
- Great for educational projects and science blogs
- Perfect for space enthusiasts and students
- Explains why interplanetary travel is still so challenging
- Demonstrates relativity between speed, time, and distance
🧑🚀 Fun Facts About Space Travel
- The Voyager 1 spacecraft, traveling at around 61,000 km/h, would take over 75,000 years to reach Alpha Centauri.
- The Moon, however, can be reached in just 3–4 days at a typical spacecraft speed.
- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko became the first person to spend over 1,000 days in space (as of 2024).
🧮 Formula Recap
\(\text{Time (hours)} = \frac{\text{Distance (km)}}{\text{Speed (km/h)}}\) \(\text{Years} = \frac{\text{Time (hours)}}{365.25 \times 24}\)These simple equations drive the calculator’s logic behind every result card.
💬 FAQs – Space Travel Time Calculator
How long is 1 year in space?
It depends on the planet. For example, 1 year on Mars = 687 Earth days, while 1 year on Neptune = 60,190 Earth days.
How is 1 hour in space equal to 7 years on Earth?
That concept comes from Einstein’s relativity theory, popularized by the movie Interstellar. It’s only possible near a black hole, not in normal space travel.
How long would 5 years in space be on Earth?
If you travel at near-light speeds, time dilation occurs — 5 years for you might equal hundreds on Earth. But at normal spacecraft speeds, time passes almost the same.
How old would I be on Mars?
You’d be slightly younger in Earth years, since a Martian year is almost 1.88 times longer than Earth’s.
🌏 Final Thought
The Space Travel Time Calculator offers an exciting window into interplanetary travel.
It turns astronomical distances into understandable timeframes – helping you explore how long it might take to journey beyond our planet using current or future technology.
If you loved this, also explore: